Induction Hardening
Induction hardening is a surface-hardening process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat the surface of a metal component rapidly, followed by quenching to increase hardness. It enhances wear resistance, fatigue strength, and durability without affecting the toughness of the core.
1. How Induction Hardening Works
Step-by-Step Process
-
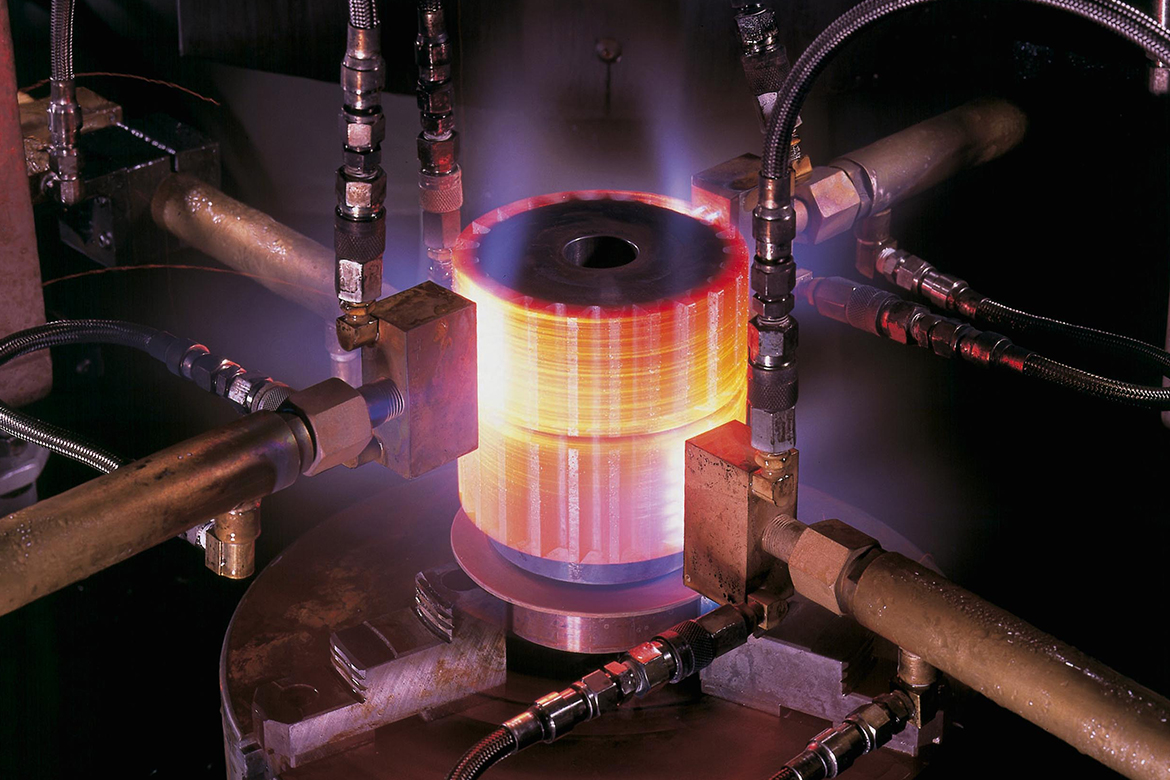
1. Electromagnetic Induction Heating
○ An alternating current (AC) passes through a copper induction coil.
○ This creates a magnetic field, inducing eddy currents in the workpiece.
○ The metal surface is rapidly heated to the hardening temperature (800–1000°C). -
2. Austenitization
○ At high temperatures, the steel structure transforms into austenite (soft phase).
-
3. Quenching
○ The heated surface is quickly cooled using water, oil, or polymer quenching.
○ This causes the austenite to transform into martensite (hard phase). -
4. Tempering (Optional)
○ To reduce brittleness, the part can be reheated to 150–300°C for controlled hardness.
2. Advantages of Induction Hardening
✅ Selective Hardening – Only specific areas of a part are
hardened.
✅ Fast Process – Heat treatment takes only seconds to
minutes.
✅ Minimal Distortion – The core remains unaffected, reducing
warping.
✅ Improved Wear Resistance – Extends the life of components.
✅ Energy Efficient – Direct heating reduces energy
consumption.
✅ Automated & Repeatable – Ideal for mass production.
3. Applications of Induction Hardening
🔹 Automotive Industry – Crankshafts, camshafts, gears,
axles.
🔹 Aerospace Components – Landing gear, turbine shafts.
🔹 Machine Tools – Spindles, bearings, cutting edges.
🔹 Railway Industry – Train wheels, rails, shafts.
🔹 Defense & Firearms – Barrels, slides, hammer surfaces.
4. Types of Induction Hardening
A. Single-Shot Induction Hardening
● The entire workpiece is hardened in one heating cycle.
● Used for small or simple-shaped components.
B. Progressive (Scanning) Induction Hardening
● The part is moved through the coil to harden specific sections.
● Used for long parts like shafts & axles.
5. Induction Hardening vs. Other Hardening Methods
| Feature | Induction Hardening | Flame Hardening | Carburizing | Nitriding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic Induction | Direct Flame | Carbon Diffusion | Nitrogen Diffusion |
| Speed | Fast (Seconds-Minutes) | Slow | Slow (Hours) | Very Slow (10–100 hours) |
| Surface Hardness | 50–65 HRC | 45–55 HRC | 55–62 HRC | 55–70 HRC |
| Distortion | Low | High | Medium | Very Low |
| Best for | Shafts, gears, camshafts | Large machine parts | Gears, bearings | Aerospace, high-precision tools |
6. Induction Hardening Depth & Hardness
| Material | Hardening Depth | Typical Hardness (HRC) |
|---|---|---|
| 1045 Steel | 1–3 mm | 50–55 HRC |
| 4140 Alloy Steel | 2–5 mm | 55–60 HRC |
| 4340 Alloy Steel | 2–6 mm | 55-62 HRC |
| Ductile Iron | 1-4 mm | 45-50 HRC |

